Total points
possible= 100 pts. The number of points for each question is shown. There are 38 questions on this exam.
Multiple Choice (2 pts each)
1)
Which of these is a correct
representation of the hierarchical organization of life
from least to most complex?
A)
hydrogen, water, heart muscle cell, nucleus, heart muscle tissue, heart, human
B)
water, hydrogen, nucleus, heart muscle cell, heart muscle tissue, heart, human
C) hydrogen, water, nucleus, heart muscle cell, heart muscle
tissue, heart, human
D)
nucleus, hydrogen, water, heart muscle cell, heart, heart muscle tissue, human
E)
hydrogen, water, nucleus, heart muscle cell, heart, heart muscle tissue, human
2)
Which of the following is reflective of
the phrase "the whole is greater than the sum of its parts"?
A) emergent properties
B)
reductionism
C)
the cell theory
D)
evolution
E)
homeostasis
3) Which of the following utilize DNA as their
genetic material?
A) archaea
B) eukaryotes
C) prokaryotes
D) A and C only
E) A, B, and C
4) Once labor begins in childbirth, contractions
increase in intensity and frequency until delivery. Therefore, the increasing labor contractions of childbirth are an example of
A) positive
feedback.
B) a feedforward mechanism.
C) negative feedback.
D) feedback inhibition.
E) both C and D.
5) What are the two classifications of
prokaryotes?
A) Domain Bacteria and
Kingdom Monera
B) Domain
Bacteria and Domain Archaea
C) Domain Bacteria and
Domain Eukarya
D) Domain Eukarya and Domain
Archaea
E) Domain Archaea and
Kingdom Monera
6) A rose bush is classified into Domain
__________ and Kingdom __________.
A) Eukarya ...
Plantae
B) Eukarya .... Protista
C) Bacteria ... Archaea
D) Eukarya ... Fungi
E) Eukarya ... Animalia
7) How are most unicellular eukaryotes
classified?
A) Monera B) Eukarya C) Archaea D) Protista E) Bacteria
8) Natural selection
A) does not require genetic
variation.
B) does not require
inheritance.
C) is not descent with
modification.
D) requires a small population
size.
E) is
differential reproductive success.
9) Each element is unique and different from
other elements because of its
A) atomic weight.
B) atomic
number.
C) mass number.
D) Only A and B are correct.
E) A, B, and C are correct.
10) How does one refer to an atomic form of an
element containing the same number of protons but a different number of
neutrons?
A) isotope
B) radioactive
C) isomer
D) ion
E) polar atom
11) How many electrons would be expected in the
outermost electron shell of an atom with atomic number 17?
A) 17 B) 2 C) 5
D) 8 E) 7
12) A covalent chemical bond is one in which
A) outer-shell electrons of
one atom are transferred to the inner electron shells of another atom.
B) protons or neutrons are
shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both.
C) the inner-shell electrons
of one atom are transferred to the outer shell of another atom.
D) electrons are removed
from one atom and transferred to another atom so that the two atoms become oppositely
charged.
E) outer-shell
electrons are shared by two atoms so as to satisfactorily fill the outer
electron shells of both.
13) The ionic bond of sodium chloride is formed
when
A) sodium and chlorine both
lose electrons from their outer valence shells.
B) chlorine
gains an electron from sodium.
C) sodium and chlorine share
an electron pair.
D) sodium gains an electron
from chlorine.
E) chlorine gains a proton
from sodium.
14) When two atoms are equally electronegative,
they will interact to form
A) ions.
B) polar covalent bonds.
C) equal numbers of
isotopes.
D) ionic bonds.
E) nonpolar covalent bonds.
15) What is the maximum number of hydrogen bonds a
water molecule can form with neighboring water molecules?
A) two B) one C) three D) five E) four
16) Which bonds must be broken for water to
vaporize?
A) polar covalent bonds
B) hydrogen
bonds
C) nonpolar covalent bonds
D) ionic bonds
E) Both C and D are correct.
17) One mole (mol) of a substance is equal to
A) 6.02 x 10 to power of (23) molecules of the
substance.
B) the largest amount of the
substance that can be dissolved in 1 L of solution.
C) Answers A and
D are correct.
D) the molecular weight
of the substance expressed in grams. One mol of glucose is equivalent to 180
g of glucose.
E) 1 g of the substance
dissolved in 1 L of solution.
18) Assume that acid rain has lowered the pH of a
particular lake to pH 5.0. What is the hydroxide ion concentration of this
lake?
A) 1 x 10 to power of (-9) mol of hydroxide ion per
liter of lake water
B) 5.0 M with regard
to hydroxide ion concentration
C) 9.0 M with regard
to hydroxide ion concentration
D) 1 x 10 to power of (-5) mol of hydroxide ion per
liter of lake water
E) Both B and D are correct.
19) Which property of the carbon atom gives it
compatibility with a greater number of different elements than any other type
of atom?
A) Carbon has six to eight
neutrons.
B) Carbon forms ionic bonds.
C) Carbon has
a valence of 4.
D) Only A and C are correct.
E) A, B, and C are correct.
20) The reactivity of an
atom is due to
- The number of electrons in the outer shell
- The number of neutrons in the nucleus
- The
number of unpaired electrons in the outer shell
- The number of electrons in the outer shell
- The number of electrons in a given atom
Fill in the blank.
21. (5 pts) List five common functional groups found in carbon-based molecules
a.________phosphate___________
b._________hydroxyl__________
c.____________carbonyl_______
d. _________amine__________
e. __________shufhydryl_________
22. (3 pts) Life has been classified into three domains. List these domains.
a. ______Eukarya______________
b. ______Bacteria___________
c. ______Achaea______________
23. (2 pts) List the
four atoms most common in living creatures.
a. _____N_______
b. _____C_______
c. ______O_______
d. ______H_______
24. (4 pts) Name the components of the amino acid shown below
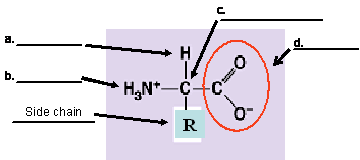
25. (4 pts) Label each amino acid
with one of the following terms: acidic, basic, polar, nonpolar
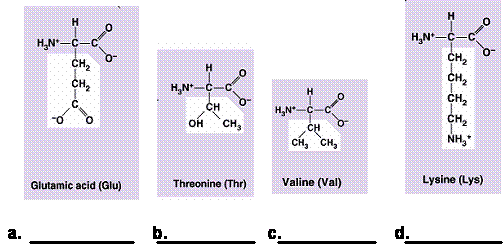
acidic polar nonpolar basic
26. (4 pts) Match the description with the type of
protein structure
A.
Primary B. quaternary C. secondary D. Tertiary
_____B_____ - the aggregation of
two or more proteins
_____A.______- the amino acid sequence
______C_____- hydrogen bonding along the polypeptide backbone
______D_____- interactions between R group side chains in the polypeptide
27. (3 pts) List three factors that can cause
a protein to denature.
a.
_____temperature, pH, salt concentration
b.
____________________
c.
____________________
28. (15 pts) Place the appropriate letter next to the description given.
List of terms
A. hydrophobic B. fats C. solvent D. dehydration reaction
E. hydrolysis F glycogen G. cellulose H. glycosidic linkage
M.unsaturated fat N. solute O.hydrophilic P.triacylglyceride
_____B____ Contains glycerol and fatty acids
_____J____ A three carbon molecule with a hydroxyl group attached to each
_____L____ Consists of only carbon and hydrogen atoms
_____A.____ A term meaning “water-repelling”
_____O___ A term meaning “ water loving”
_____C____ The dissolving agent in a solution
_____N____The agent being dissolved in a solution
______G____A carbohydrate storage polymer in plants
_____F_____A carbohydrate storage polymer in animals
______H____The name given to the bond between sugar monomers
______P____Three fatty acids joined to a glycerol molecule
______I____A carbohydrate used to form the exosketeton of insects
______D____The generation of macromolecular polymers
______E____The degradation of macromolecular polymers
_______M___Contains one or more double-bonded carbons
True/False: Circle the correct answer (2 pts each, total 20 pts)
29. T F 32
P and 33P are referred to as isomers because they differ in the
number of protons.
30. T F The electron shell next to the nucleus has the
highest potential energy
31. T F The valence of 8O (oxygen) is 4.
32. T F Water has polar covalent bonds between atoms
33. T F Ionic bonds tend to share electrons in order
to complete their valence shells
34. T F The formula O2 is an example of a structural formula.
35. T F Chemical reactions are described in terms
of reactants and products
36. T F Evaporative cooling refers to the cooling of
the atmosphere as water evaporates.
37. T F Saturated fats tend to be associated with cardiovascular
disease.
38. T F Phospholipids consist of two fatty acids,
glycerol and a phosphate group.